Active Directory Migration Tool can be used to migrate users, groups, and computers between Windows NT domains and Windows 2000 domains. The process of migrating users, groups, and computers is referred to as domain migration.
An interforest migration is any move from a domain outside of a particular forest to a Windows 2000 domain inside that forest. Because Windows NT domains are not part of a forest, migrating users, groups, and computers from a Windows NT domain into a Windows 2000 domain is considered an interforest move.
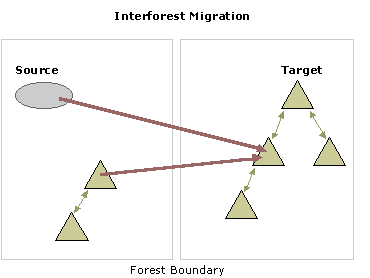
Interforest migration flowchart
As shown in the illustration, moving security principals or resources from any of the domains on the left of the forest boundary (source domains) into any of the domains on the right (target domains) is an interforest move because the source and target domains are not in the same forest.
Interforest migration flowchart
Most organizations that are currently using Windows NT have account domains and resource domains. As shown in the illustration, the steps to perform an interforest migration include migrating the user and group accounts in the account domains; migrating the service accounts, local profiles, and shared local groups in the resource domains; and then updating the rights of the migrated users. When the migration is complete, the source domains can be decommissioned, and the computers can be moved into the target domain. Essentially the same steps can be used to migrate Windows 2000 domains from one forest into Windows 2000 domains in a different forest.
For information about preparing domains for migration, see Migration requirements and Before performing an interforest migration.
For details about migrating domains between forests, see To perform an interforest account domain migration, To perform an interforest resource domain migration, and the Microsoft Web site (http://www.microsoft.com/).